Cables and Stranded Wires: An Introduction with Stäubli
Stranded wires are essential components in the fields of electricity and electronics. They serve to transmit electrical energy as well as informative data, enabling the functionality of modern devices, systems, and the entire power grid. Whether in households, industrial settings, communication devices, or transportation systems, the level of technology and comfort we are accustomed to would be unthinkable without wires.
Fundamentals of Stranded Wires
Structure and Materials
Stranded wires consist of thin conductors (known as strands), which are typically made from copper or aluminium due to their excellent electrical conductivity. The stranded wires are surrounded by insulation to prevent short circuits and electrical discharges and to protect the conductors from external influences such as moisture.
When combined with flexible insulating materials, this results in exceptional flexibility of the wire. This flexibility makes stranded wires particularly suitable for applications where wires need to bend frequently, such as in the moving parts of machines (e.g. robots) or in portable devices.
Types of Wires
There are various types that exhibit different properties based on their applications. Power cables, data cables, coaxial cables, and fibre optic cables are just a few examples. Each cable is optimised for its specific application, whether for transmitting high electrical power or sensitive data.
Application Areas and Specifications of Stranded Wires
- Household and Industry: In buildings, power cables are often installed within walls and floors to supply energy to sockets and light switches. In industrial applications, specialized cables and stranded wires are often required to have higher load-bearing capacities and resistance to chemical or mechanical influences (e.g. made of silicone).
- Data Transmission: Data cables such as twisted-pair cables, coaxial cables, or fibre optic cables are designed to transmit data as quickly and interference-free as possible. They are used in networks, for internet connections, and in telecommunications.
- Standards: Wires are subject to strict standards that ensure quality, safety, and interoperability. These regulations are established by international and national standardisation bodies such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
Challenges and Innovations in Stranded Wires
- Safety Aspects: Fire safety regulations are particularly important, as defective wires can cause fires, damage equipment, and endanger lives. Consequently, fire-resistant materials and constructions are being developed to mitigate these risks.
- Sustainability: With the increasing importance of environmental protection, awareness of sustainable wire production and disposal is also growing. Research focuses on recyclable materials and methods for recovering metals from used wires.
- Innovations: New technologies, such as nanotechnology, promise more efficient and lighter wires. Additionally, wireless technologies like inductive charging present new opportunities for reducing reliance on wires in certain applications.
The Role of Stranded Wires in Electrical Infrastructure
Stranded wires and cables are indispensable components of electrical infrastructure, with versatile application areas and technological challenges. Future developments will continue to enhance the performance and safety of wires, while alternative technologies will provide additional solutions.
The significance of these components is paramount as long as electrical energy and data transmission play a crucial role in our society.
Stranded Wires from Stäubli
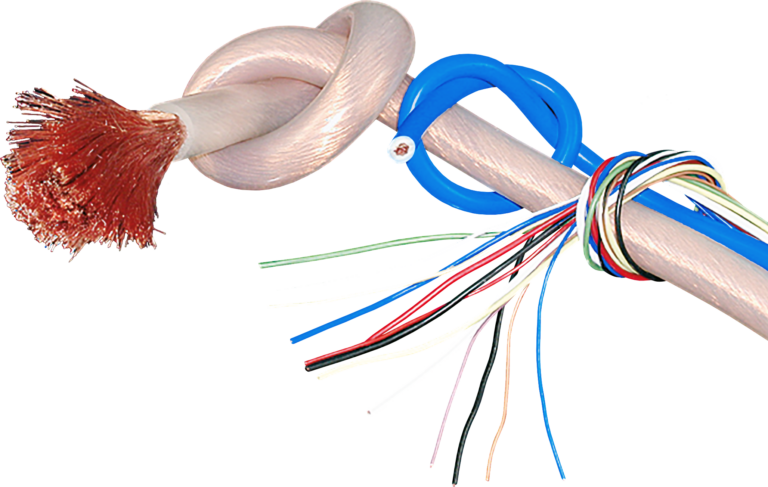
Stäubli manufactures both test leads and various other stranded wires in Essen and processes not only PVC but also silicone as sheath materials.
With their specialised machinery, Stäubli produces cross-sections of up to 95mm². These wires consist of finely stranded conductors and soft silicone, making them flexible and particularly easy to install.
Challenges often arise, particularly when laying wires in small and tight radii, such as in the fields of e-mobility or robotics in automation, where flexibility plays a central role. These challenges are taken into account during product development at Stäubli.
The range of cross-sections is as wide as the range of applications for the strands. Stäubli wires are suitable for common applications in measurement technology, but also for e-mobility. The wires are especially well-suited for the confined spaces of battery packs in cars, buses, and trucks.
Stäubli’s silicone wires are ideal for tight bending radii, higher temperatures, and sharp edges. They can be loaded up to a maximum of 20,000 V AC (SILI-HV 6.0) or 290 A (SILI-S 95).
Safety of End Users
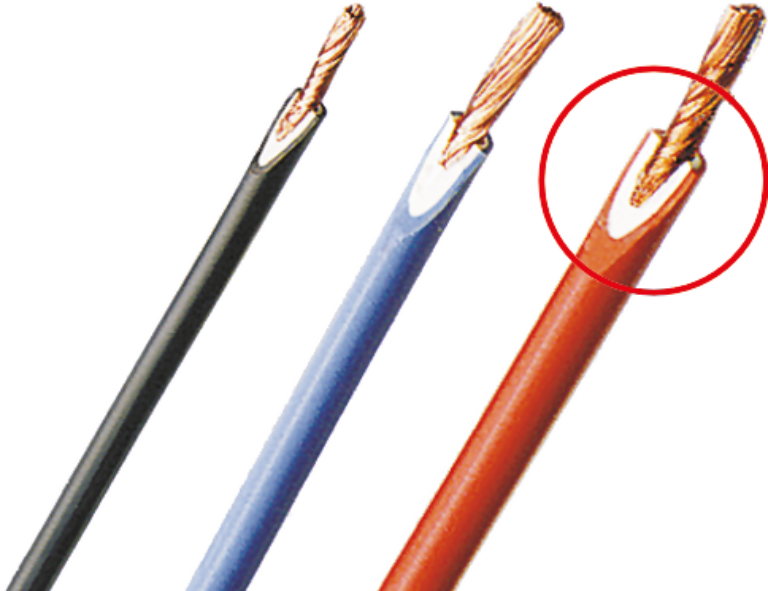
A core theme at Stäubli is the safety of end users, as the products are primarily used manually—this concerns human lives. “Safe to use” is the guiding principle here.
Accordingly, several aspects such as UL certification and dielectric strength are immensely important. In production, every metre of wire is tested for dielectric strength.
As an additional feature, the manufacturer offers test leads with double-layer insulation (white inside, coloured outside). This allows for easy detection of damages to the outer insulation layer, which may occur over the product life cycle (wear and tear). This facilitates timely replacement of the wires.
Sustainability
Sustainability is another area that Stäubli is actively working on. In addition to photovoltaic systems on the company buildings and the transition of the company fleet to electric vehicles, waste reduction in the production environment is a central task.
Stäubli collects the scrap generated during production, which is reintroduced into the production cycle. Stranded wires are separated into copper and sheath material, allowing Stäubli’s partners to reuse these materials in an environmentally friendly manner.
These optimisations are a key element for a continually greener CO2 footprint.
In summary, the stranded wires from Stäubli offer:
- wide range of cross-sections
- numerous colours
- sheath materials of PVC and silicone
- compliance with standards such as UL
- recycling of scrap
- technical load capacity
- flexibility of the wire





