ESD Protection Measures at the Workplace
To prevent electronic components from being damaged by electrostatic discharges, targeted ESD protection measures are necessary in the workplace. But which measures are really effective? In this article, you will find everything you need to know about ESD protection in the workplace - from the right clothing and suitable tools to optimal room design.
How to protect electronic devices from electrostatic discharge
Depending on the voltage it can be felt, heard, and even seen: the electrostatic discharge. While most discharges take place below the threshold of human perception, they can still cause great damage in electronic components. To prevent this, extensive ESD protection measures are necessary.
What is ESD?
Who does not know the moments when electrostatic voltage is discharged: a crackling sweater, hair “standing on end” or the electric shock at the car door? This discharge is called Electrostatic Discharge, or ESD for short.
It can often be felt in everyday life, for example when walking with rubber soles over a carpet. In this case, mainly negative electric charges are absorbed. These are distributed over the entire object or body. As soon as there is contact with another conductive body or grounding, the charge flows away abruptly.
The electrostatic discharge therefore occurs when two different materials meet or separate. In industrial processes, a discharge can be observed, for example, when adhesive tapes are unrolled, or conveyor belts are moved.
The electrostatic charge is promoted by low humidity. Therefore, the humidity in the room should always be between 50 and 60 percent.
What risks does ESD entail?
While discharges are not a problem in everyday life, they are a major hazard for the electronics processing industry. During the production of electronic assemblies and devices, ESD can lead to invisible defects on the component or even to a total loss. The consequences: Production downtimes, high repair and manufacturing costs, customer dissatisfaction and loss of product reputation. According to statistics, around 25 percent of all electronic components are returned to the manufacturer due to ESD damage – a figure that makes ESD protection measures in production plants seem almost indispensable.
Which industries need ESD protection?
ESD protection measures are useful and necessary in almost every work area: whether in the laboratory, in production, in manufacturing or in the warehouse. Workstations in technical customer service and on assembly sites are also tested for ESD resistance. Among the industries in which ESD protection measures are particularly important are the electronics industry, computer technology and telecommunications, as well as the automotive industry.
Regulations and guidelines for an ESD workstation
DIN EN 61340-5-1 is the standard for ESD workplaces in Germany and in many European countries. It contains guidelines for “Protection of electronic components against electrostatic phenomena” and enables companies to effectively manage electrostatic discharges. The ESD standard describes all necessary conditions for creating, establishing, and maintaining a control program regarding ESD for electrical and electronic parts, components and devices.
It also shows how Electrostatic Protected Areas (EPAs) must be equipped to allow work with electrostatically sensitive components without damaging them.
How does ESD protection work?

In order to avoid ESD damage, it is essential to process ESD-hazardous components, such as light-emitting diodes, semiconductors or integrated circuits, exclusively in a protected environment – an EPA (Electrostatic Protected Area). Packaging and storage should also take place solely in these special premises. Only in ESD workplaces can it be ensured that charges are prevented and one can discharge electrostatic charges in a controlled manner, for example by grounding the bodies. Therefore, components such as work surfaces, furniture, clothing, shoes or floor coverings should be electrically conductive. Bürklin has been working with ESD-Protect GmbH in this area for many years. As a result, we can offer companies a comprehensive portfolio of high-quality ESD products.
The ESD workstation
According to the ESD standard, workplace-related ESD protection measures are for example:
- Dissipative or antistatic work surfaces
- Electrostatic protective floors
- Remove unnecessary insulators such as coffee cups, adhesive tapes or styrofoam from the workplace
- Check all equipment and operating resources within the ESD protection zone for necessity and ESD-compliant behavior
- Always wear a wrist grounding strap when performing sedentary tasks
How does ESD clothing work?
Employees can cause an electrostatic charge by moving or rubbing against other bodies. To prevent this, special dissipative protective clothing should be worn in the protected environments. This is usually made of cotton or special fabric with conductive yarn fibers.
Important: The protective ESD clothing must always be worn close to the body and closed. The clothing underneath must not be visible, otherwise the protective effect would be nullified.
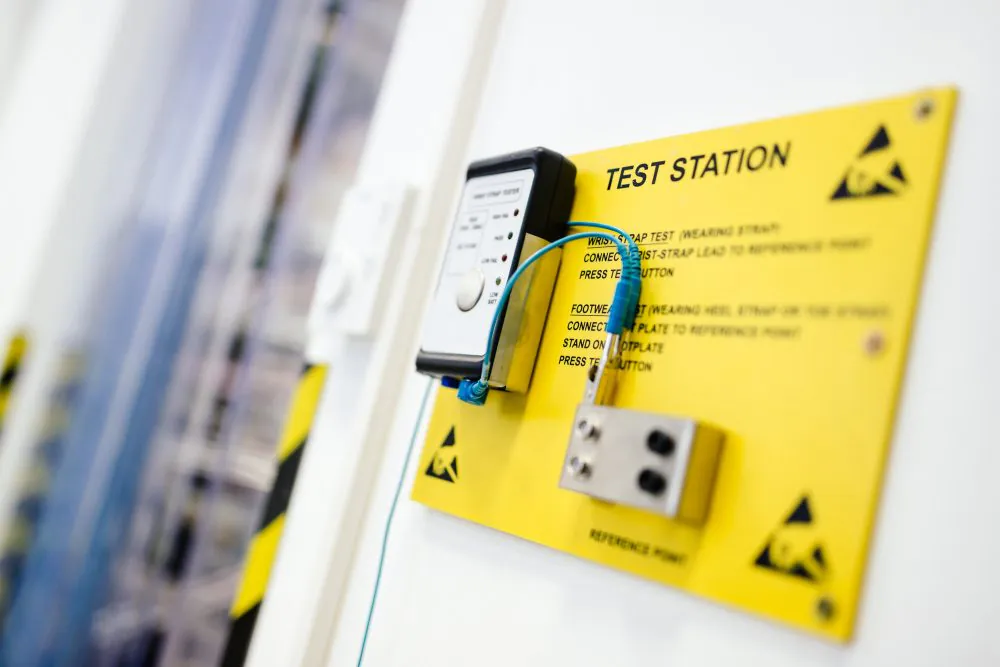
ESD test stations and ionizing units: Effective protection against electrostatic discharges
ESD test stations and ionizing units are important components in the field of ESD protection. They are used to protect electronic devices from electrostatic discharge. Test stations are used to check the ESD sensitivity of components and products and ensure that they meet the required standards. Ionizers, on the other hand, neutralize static charges in the environment to prevent damage to sensitive electronics. Overall, these technologies are essential for companies that work with electronic components and want to ensure effective ESD protection.
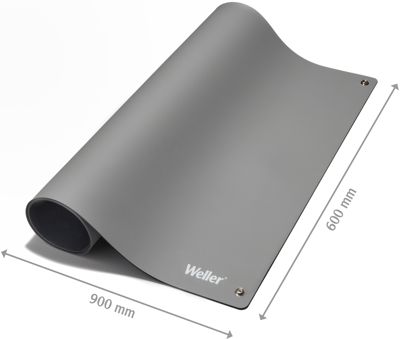
Effective ESD protection: Quick-to-use coverings for maximum safety in small ESD protection zones
ESD table and floor coverings offer maximum safety against electrostatic discharge. It is particularly important for users in assembly and quality assurance to protect themselves from ESD hazards. For this reason, quick-to-use table and floor coverings are an ideal solution for smaller ESD protection zones. These coverings can prevent potential damage caused by electrostatic discharge. They ensure that the electrical charge is safely dissipated, thus protecting sensitive electronic components.
Thanks to their antistatic properties, they also reduce the risk of malfunctions or failures in sensitive devices. The ESD coverings are easy to install and offer reliable protection against electrostatic discharge.
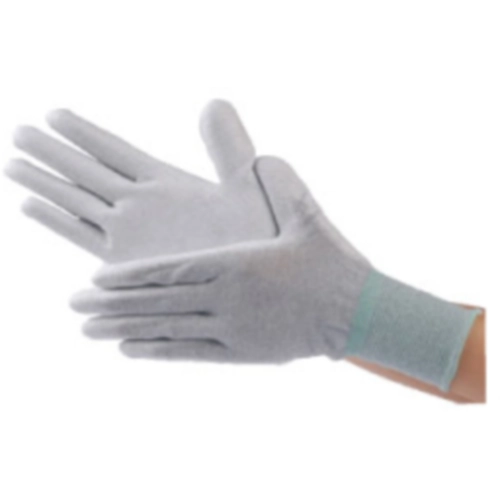
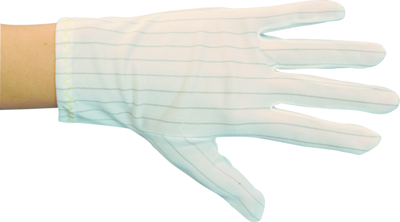
ESD shoes and gloves
In addition to the clothing, shoes must also comply with EPA guidelines. These are dissipative models that dissipate electrical charge via the floor to the earth potential.
The use of ESD gloves means that the charge is not accumulated but is permanently dissipated each time contact is made with an earthed surface. They are characterized by low charge generation and a high degree of charge dissipation.
ESD tools
All tools in use in an ESD protection zone should be largely conductive. This means that the handles are not made of plastic or metal as usual, but of electrostatically conductive materials. This way, when contact is made with a component, a slow charge equalization occurs, which prevents ESD damage.