The Fascinating World of Tweezers: How to Choose the Right Ones
There is a wide range of different types of tweezers, with several hundred different models available. What are the main features that help you choose the right tweezers for the task at hand? We take a closer look at this fascinating world and give you tips on how to choose the right tweezers for your application.
Tweezers: Masters of Precision
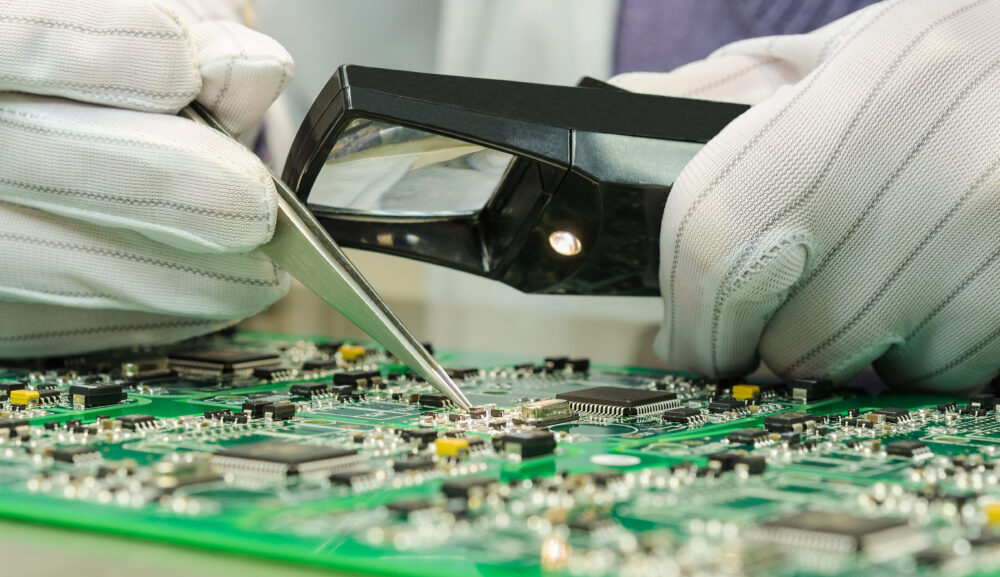
Tweezers are used as an extension of the fingers to concentrate gripping force and perform a variety of tasks with precision. They are used when objects are too small, too fragile, too hot, too cold or too corrosive to hold, place or remove directly with the hands.
The production of tweezers can involve up to 25 steps, depending on the chosen shape and the materials used. Each of these steps ensures that the finished tweezers meet the highest standards of precision and quality.
When choosing tweezers, the following aspects in particular should be taken into account:
- Ergonomics: A well-designed tweezer should be comfortable to hold and minimise fatigue.
- Reliability: It should deliver consistent results and reliably fulfil its function over long periods of time.
- Durability: High-quality materials and workmanship ensure a long service life.
- Performance: The tweezers should grip and hold precisely without damaging the material being worked on.
- Area of application: The specific shape and material should be suitable for the respective application.
What types of tweezers are there?
There are about 30 different families of tweezers. The most common ones are general-purpose tweezers and high-precision tweezers, which are used in almost all industries and markets.
In addition, each industry has specific requirements for the hand tool:
- Medical technology: Here, cutting tweezers are the most common, as they enable precise cutting and holding.
- Life sciences: In this area, wafer tweezers are particularly in demand for safely handling sensitive samples.
- Electronics industry: SMD tweezers and tweezers with interchangeable tips are of the utmost importance here for precisely placing the fine and sensitive components.
The wide range and specialised use of tweezers shows how important it is to choose the right tweezers for the task at hand in order to work precisely and efficiently.
The delicate art of precision: How to choose the perfect tweezers
Choosing the right tweezers is a crucial basis for precise work in many areas. The requirements are just as diverse as the tasks they have to fulfil. A well-chosen pair of tweezers not only makes it easier to handle delicate or hard-to-reach objects, but also contributes significantly to the quality of the work.
Tweezer geometry: what the international code tells us
The shape of tweezers is clearly defined by an international code. Codes such as 2A, 7 or 15AGW describe the shape and composition of the tip. The tip type can be recognised with the naked eye, regardless of the manufacturer, material or coating. This shape in turn determines the respective tweezer family.
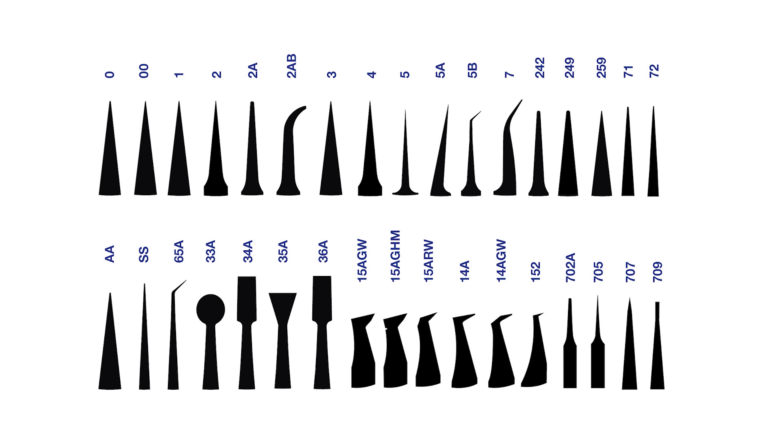

The 2A style, also known as the ‘duckbill’ style, is for example flat with a rounded tip. The most common material variant is ‘SA’ (acid-resistant and antimagnetic stainless steel).
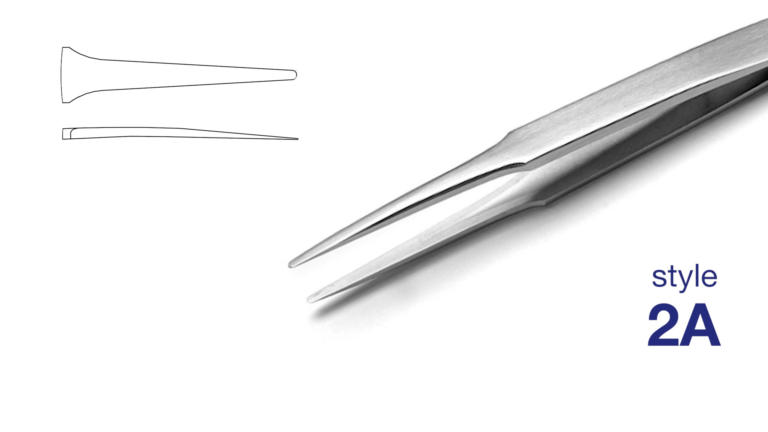
However, 2A tweezers can also be gold-plated, diamond-coated, Teflon-coated, epoxy-coated, made with ESD rubber or foam handles, with plastic or ceramic tips, or even be made of titanium. However, the shape of the tip always remains flat and rounded.
Two other very common types are 5 and 7. Type 5 has straight, sharp and extremely fine tips, while type 7 has curved, very fine tips that provide maximum visibility during use.
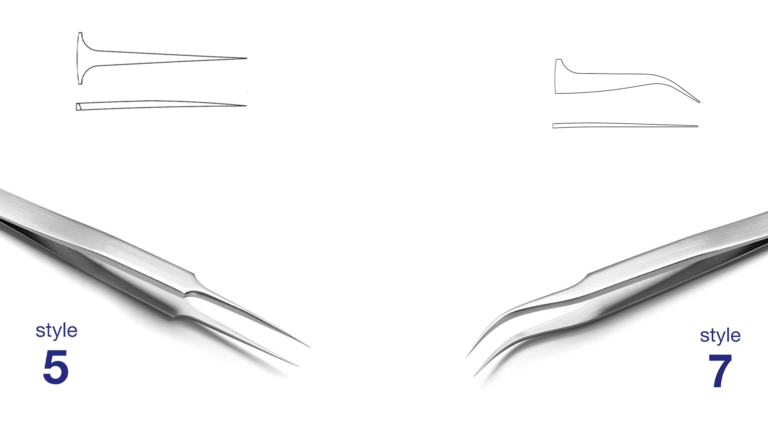
Some styles are used in almost every market, while other styles are used mainly in certain markets or even only for very specific applications.
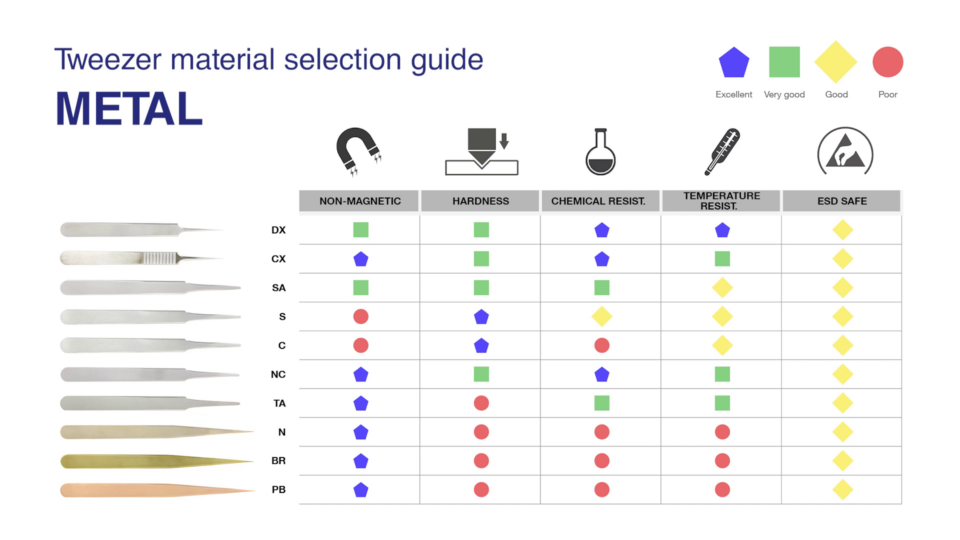
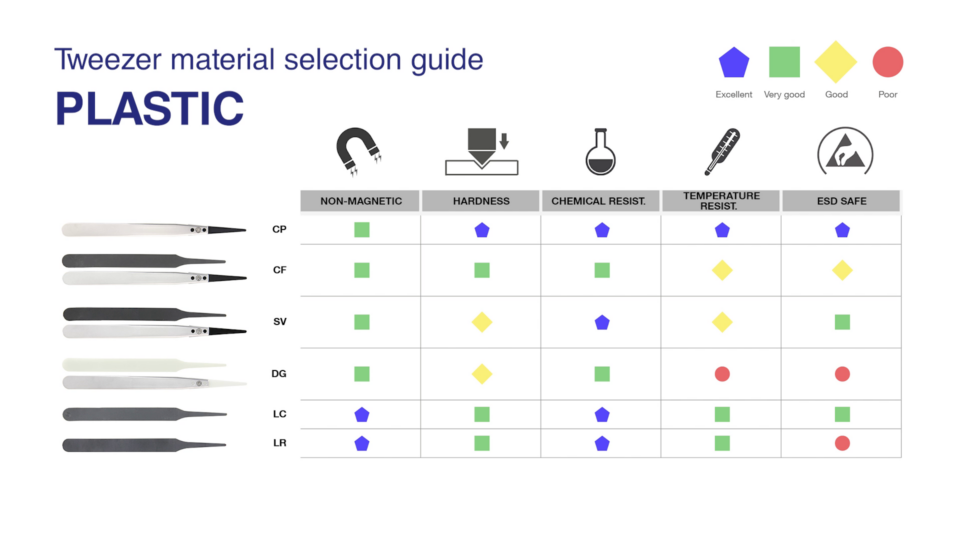
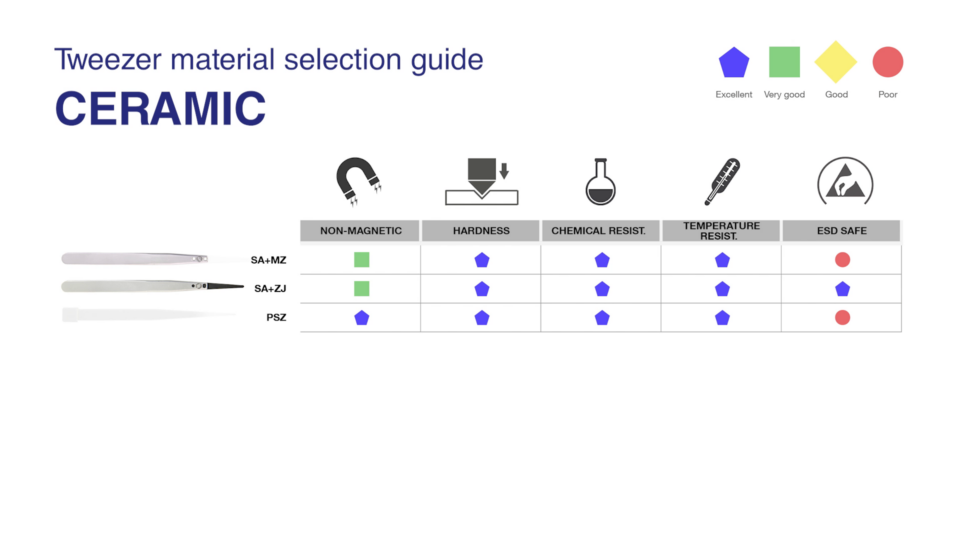
Material selection for tweezers: From stainless steel to titanium
In addition to the shape, the choice of the right material is also crucial in selecting the right tweezers. There are a variety of materials available for manufacturing tweezers, including: stainless steel, antimagnetic and acid-resistant stainless steel, carbon steel, high-alloy stainless steel, superalloys, plastic, ceramic, carbon fibre, nickel, brass, bronze and titanium.
The most important properties of the tweezers, such as anti-magnetic properties, hardness, corrosion and chemical resistance, temperature resistance, ESD properties, biocompatibility or suitability for use in clean rooms, depend on the material used.
The most common materials include
- SA (acid-resistant and antimagnetic stainless steel): SA is mainly used when corrosion resistance and robustness are the primary requirements.
- Carbon steel: Carbon steel is particularly important when strength and hardness are the main considerations, for example in cutting tweezers for cutting through hard wires.
- Superalloy (CX): Superalloys are required in very aggressive chemical environments.
- Titanium (TA): Titanium is ideal for handling components during cleaning and chemical processes at very high temperatures, in histology and biology. The material is mainly used when a high strength-to-weight ratio is required.
- Plastic: Plastic tweezers are made from a variety of plastics including carbon fibre, carbon-PEEK, nylon, PVDF and Delrin.
- Ceramic: Ceramic tip tweezers are suitable for high temperature applications and handling delicate components during thermal and chemical processes, as well as ceramic and glass components where it is critical that no metallic scratches occur.
ideal-tek uses only high-quality materials for its plastic tweezers. All plastic products are manufactured in-house using injection moulding. The manufacturing processes are carefully monitored and quality-controlled at the production stage.
From diamond to gold: coatings for every application
Some tweezers are coated to improve their physical, ergonomic, chemical or technical properties. This is a decisive factor for certain applications.
Diamond coating (DC)
Diamond coatings are biocompatible and are ideal for applications in medical, biological and cleanroom environments. They are also suitable for handling hard and abrasive materials, as they prevent any possible particle or metal contamination.
ESD epoxy resin coating
An ESD epoxy resin coating (NE) helps to dissipate electrostatic charges and increases operating comfort. In the case of carbon steel tweezers, such as cutting tweezers, the coating also prevents the formation of rust.
PTFE coating
PTFE is a material similar to Teflon. The coating is used in very aggressive chemical environments and for critical cryogenic work to reduce thermal conductivity.
ESD rubber handle coating (DR)
A rubber or foam grip coating improves the ESD properties of the tweezers and makes them perfectly conductive. In addition, this type of coating improves the ergonomics of the tweezers, making them ideal for repetitive work.
Gold-plated coating (GP)
In the gold-plating process, tweezers are coated with a 2-micron layer of pure 24-carat gold. This makes the tweezers resistant to chemical corrosion and oxidation and provides excellent electrical conductivity. Gold-plated tweezers are used in microelectronics, TEM staining, immunogold work, electrochemistry and nanotechnology.
Cutting tweezers in the medical field: precision in a confined space
Cutting tweezers are an important element in the manufacturing of medical devices. They are indispensable for reaching and precisely cutting wires, especially hard wires, in confined spaces.
ideal-tek offers three different types of cutting blades, depending on the application: angled cutting blades, parallel cutting blades and predominantly angled cutting blades. The models offer a wide range of solutions for specific cutting requirements in medical technology:
Model 15A with angled blades: The cutting surface is limited to a very small area at the tips. This allows the entire force applied by the fingers to be transferred to the tips to make an extremely precise cut.
Model 15AGW with predominantly angled blades: The blades meet mainly at the tip, which means that the cutting surface is larger than with angled cutting blades. For most cutting tasks, the user can perform their work more easily.
Both angled and predominantly angled blades are ideally suited to the limited working area under a microscope. The small contact point increases the accuracy of the blades thanks to their perfect alignment.
Model 15AP with parallel blades: The tweezers enable cutting at any point on the cutting blade, as they offer a larger contact surface. The force is not concentrated in a specific area, but distributed over the entire blade.

ideal-tek tweezers: high-quality materials and perfect workmanship
ideal-tek sets standards in precision, durability and user-friendliness with quality and craftsmanship. This makes their tweezers an optimal choice for demanding applications.
They are handcrafted to achieve perfect symmetry and alignment of the tips. This ensures a consistent point of contact, a comfortable grip and ideal weight distribution. The arms of the tweezers are identical in thickness and shape, resulting in uniform tension between the two sides.
The in-house sandblasting process gives the ideal-tek tweezers a perfect, non-reflective surface. Special attention is paid to ensuring that all tweezers have rounded edges and no sharp corners or burrs. This makes the tweezers suitable for users who wear nitrile gloves.
The tips of the tweezers are laser welded with Swiss precision and quality. This results in a higher stress resistance and a perfectly sealed product that offers no possibility of contamination. The tumbling and electropolishing processes also remove any surface contamination, and a final ultrasonic cleaning step before packaging ensures that the finished product is completely clean.
Ideal-tek tweezers are also certified in accordance with ISO 9001 and ISO 12485 (medical device certification).