MID-compliant Energy Measurement Technology: Reliable Data for the Energy Transition
Everyone is talking about energy transition and climate protection. But how can we ensure that we receive reliable data on our energy consumption? This is where energy measurement technology comes into play. Find out what role this technology plays in the energy transition and how important the MID directive is. We also introduce you to WAGO's smart MID energy meters, which make energy management easy.
Energy measurement technology: A definition
Energy measurement technology deals with methods and devices for measuring energy in various forms. These forms include electrical energy, thermal energy, kinetic energy and chemical energy. Energy measurement technology is particularly important for the measurement of electricity and heat. It plays a central role in energy management, billing and efficiency improvement.
Commonly used measuring devices in this area are electricity meters, heat meters and gas meters. These technologies make it possible to monitor and manage energy consumption.
Advanced technologies also include smart meters, which enable more detailed real-time monitoring and smart grids.
Energy measurement technology also includes methods and tools for assessing the energy efficiency of buildings and facilities, energy audits and compliance with energy directives.
The role of energy measurement technology in the energy transition and climate protection
There are several reasons why measurement technology plays a crucial role in the energy transition and climate protection:
- transparency of energy consumption: accurate measurements allow both consumers and businesses to better understand where and how energy is being consumed. This information is essential to effectively manage and reduce energy consumption.
- energy efficiency: Energy measurement technology helps to identify areas where energy efficiency can be improved. By monitoring energy consumption, potential savings can be uncovered, which in turn leads to lower CO₂ emissions.
- grid management: In the course of the energy transition, the integration of renewable energies is becoming increasingly important. Energy measurement technology makes it possible to better integrate the fluctuating energy flows from renewable sources such as solar and wind power into the electricity grid and optimize the energy flow.
- billing and pricing: More accurate metering methods can help to establish fairer energy pricing that reflects customers’ actual consumption and usage patterns. Rates that encourage energy savings (e.g. time-variable rates) are possible.
- smart grids and demand response: Modern energy measurement technology is a central component of intelligent electricity grids (smart grids). It enables “demand response” measures in which energy consumption is promoted in times of high energy availability and curtailed in times of scarce resources.
- energy audits and regulatory compliance: precise energy measurements are important for companies and organizations to carry out energy audits and comply with legal requirements.
- decarbonization: Energy measurement technology is helpful to measure the success of decarbonization measures, such as switching to less carbon-intensive energy sources or improving building insulation.
In summary, energy measurement technology enables data-driven management of energy resources, which is essential for achieving climate targets, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and successfully implementing the energy transition.
MID Directive: What does the Measuring Instruments Directive stipulate?
The MID Directive 2014/32/EU, short for “Measuring Instruments Directive”, is a European directive that sets uniform requirements for many measuring instruments. The aim of the directive is to regulate the use of measuring instruments and measuring technology in the European Economic Area (EEA).
The most important points of the MID Directive for energy meters:
- The MID Directive applies to various types of energy meters, including electrical energy meters, gas meters, water meters and heat meters.
- Manufacturers must prove that their meters comply with the requirements of the directive. This is done by means of an assessment procedure, which includes testing the design and checking the quality assurance.
- Devices that meet the requirements of the MID receive the “CE” marking and the specific “M” marking for measuring instruments. This ensures that the product complies with European standards.
- Manufacturers must provide technical documentation proving that the product is compliant. They must also ensure that production is consistent and that the devices meet the requirements on delivery.
- Measuring instruments that comply with MID regulations can be sold in any EEA member state without adaptation or testing.
- Security features must be applied to make tampering difficult. Components must be marked and protected to make openings or tampering detectable.
- The directive improves consumer protection by introducing uniform measurement standards.
- Inspection intervals: Another component of the MID is the definition of regular inspection intervals after initial commissioning. This is intended to ensure that the devices continue to measure accurately and reliably.
The MID Directive ensures high quality standards for measuring devices in Europe and strengthens confidence in consumption data. The directive thus facilitates trade and cooperation in Europe and ensures that devices are safe, accurate and reliable.
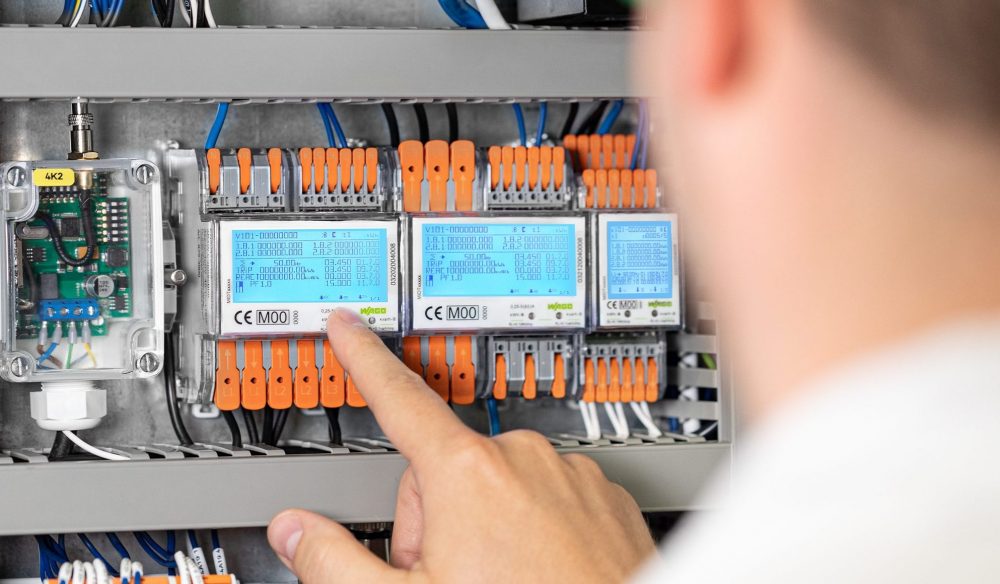
Smart meters for simple energy management: MID energy meters from WAGO
Optimizing energy consumption is not possible without comprehensive energy measurement. MID-certified energy meters from WAGO set the course for this. The energy meters offer numerous advantages:
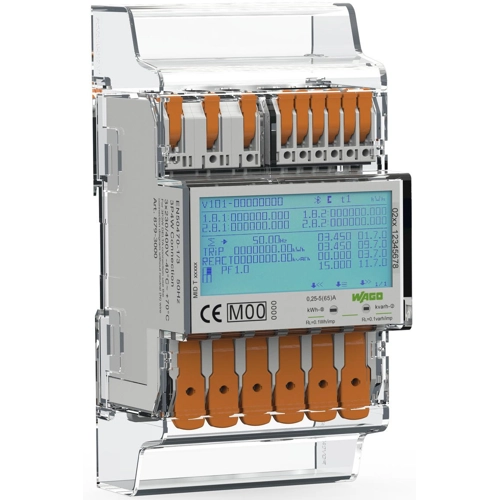
- With Push-in CAGE CLAMP® technology, the energy meters can be connected easily and quickly.
- With a width of 72 mm for direct measurement and 35 mm in the version for current transformers, the user saves a lot of space in the control cabinet.
- In addition to values for active and reactive energy, they also record the mains frequency, current, voltage and power for all phases.
- The large illuminated display shows all important measurement data at a glance.
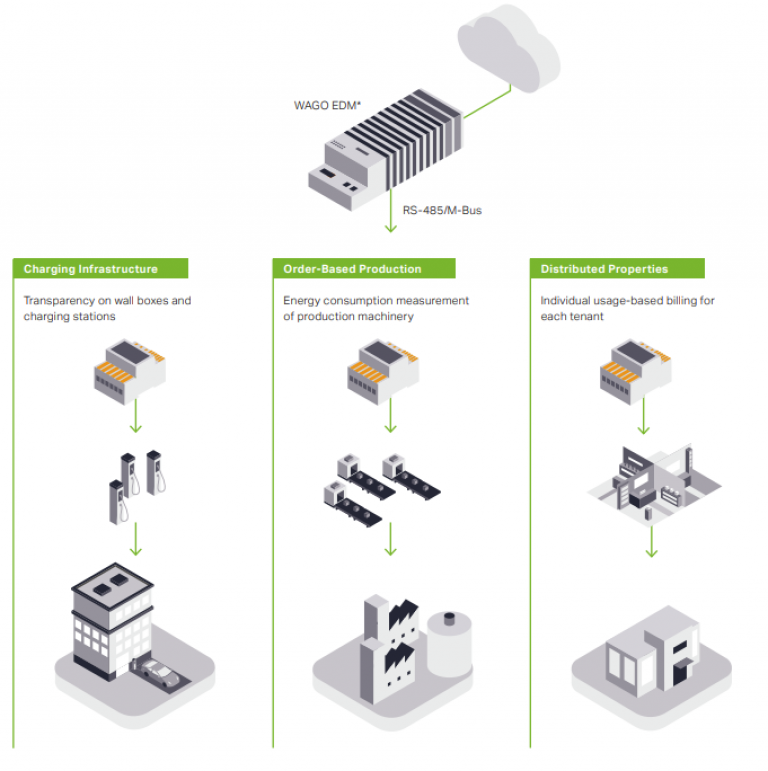
- The energy meters have various interfaces: RS-485 interface (Modbus®-RTU protocol), M-Bus, pulse output, Bluetooth®.
- Thanks to MID conformity, applications with consumption billing are also possible.

The energy meters use 4-quadrant measurement to record active and reactive power. This makes it possible to differentiate between supply and consumption. With just one energy meter, the amount of electricity supplied and purchased can be recorded precisely – whether for photovoltaic and wind power systems or conventional electricity purchases.
The energy meters are ideal for electricity billing that complies with legal regulations, takes into account different rates and reflects both supply and demand.
The smart energy meters have been developed for a wide range of applications – from use in charging stations and wallboxes, in the manufacturing industry or in the retail sector for shop-in-shop applications