Industry 4.0: Use of RFID Components
RFID in Industry 4.0 - the technology that enables products and operating resources to be managed more efficiently. In this article, you will learn what it is all about: We will show you how RFID works, what advantages it offers and where it is used.
From resource management to tracking
RFID makes a contribution to communication between man and machine – and at the same time meets the demand for cost reduction through increasing automation. From effective resource management to precise tracking, a decisive contribution is made to improving process reliability and quality. And this in very different industries.
RFID – what does it mean?
The abbreviation RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, i.e. identification by radio. A data transfer using electromagnetic waves enables communication between two devices. It is a special transmitter-receiver system with which objects and living beings can be identified and localized – automatically, without contact or visual contact.
How do RFID components work?
The reading device – the so-called reader – generates an electromagnetic alternating field to which the RFID transponder – also called tag – is exposed. The microchip integrated in the RFID transponder decodes the reader’s commands and encodes the response. The transponder influences the electromagnetic transmission field of the reader and transmits the information requested by the reader. This includes, for example, location recognition and a globally unique identification of objects. In short: radio waves transmit the data from the transponder to the reader, which makes contactless reading or writing of information possible.
The interesting thing about this is that the magnetic alternating field is not only used for data transmission, but also for supplying the transponder with energy. Costly alternatives are active transponders with their own power supply. Generally, RFID components are distinguished according to transmission frequency – high or low frequency – as well as according to manufacturer and intended use.
Advantages of RFID technology
The identification with RFID tags makes it possible,
- Collect data quickly and paperlessly and evaluate it without (visual) contact
- Eliminate write errors in recording data
- Reduce working time by reducing paperwork
- control the management of equipment and warehouses
- comply with legal requirements
- easy exchange of current information
- reliably operate systems in harsh environments (such as in the presence of moisture, dirt or vibration)
As soon as personal data is involved, these advantages are often countered by data protection concerns – RFID blockers are currently on everyone’s lips. The purpose for which RFID technology is used must therefore be carefully considered. In addition to the possible loss of informational self-determination, RFID components also have technical limitations – for example, in terms of range or the ability to determine position, direction or speed.
Where is RFID used?
Security, serialization, tracking, identification – RFID tagging is used in the following areas:
- Resource and asset management
- Theft protection and traceability
- Warehouse and logistics: inventory, inventory management and positioning
- Maintenance and servicing
- Attendance check and time recording
- Access and entry controls
- Identification of weak points
- Container management: Monitoring of refilling and filling processes
- Identification and construction status documentation of vehicles
- Rental and hire service
- Animal identification
RFID in the industry 4.0
1. Financial industry
There is hardly anyone who has not yet made use of contactless payment or at least heard of it. There is still a debate going on as to whether or not banknotes should be fitted with an RFID chip in the future. Counterfeit protection and the complete documentation of the money circulation are faced with immense costs and data protection problems.
By the way: RFID chips can also be found in every German passport and identity card as well as in the Swiss passport.
2. Textile and clothing industry
Whether clothing, shoes or sports: More and more clothing manufacturers and fashion retailers are relying on RFID to ensure transparent supply chains and to secure their goods. German-speaking RFID pioneers include the companies Levi Strauss & Co. and Gerry Weber. The use of the technology creates inventory transparency and control over the entire product lifecycle – from production and logistics to sales through various channels.
3. Food industry
What already works well in the garment industry should also be introduced in the food industry: Slowly but surely, RFID technology is approaching mass production. By precisely documenting the flow of goods, inventory levels could be optimized, food waste minimized and the traceability of the supply chain improved. Large retail chains are showing great interest.
4. Pharmaceutical industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, RFID tags help meet the detailed verification requirements with improved proof of origin. The technology also protects against counterfeiting. Another area of application is the quality control of temperature-sensitive medical products: RFID tags with sensor functions in the transport containers react to temperature, pressure or humidity – and thus document even before arrival whether the transport conditions have been met.
5. Aviation industry
In order to reduce the so-called suitcase error rate, all baggage tags in air travel are to be equipped with RFID transponders by 2020. This will enable the baggage to be precisely tracked at many more points, even without visual contact, making it easier to re-route. Misrouting and thus loss of baggage will be avoided, which will ultimately result in air travelers being more relaxed.
RFID components from HellermannTyton at Bürklin Elektronik
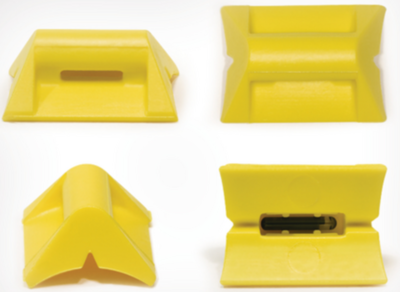
HellermannTyton is a specialist for RFID cable ties with various transponders. If you choose readers of the same brand, you can be sure that the data will be read quickly and easily. Error-free reports result in an efficient use of resources. What’s more, RFID components can be attached quickly and easily.
The HellermannTyton product range in the Bürklin online store includes
- Cable ties with integrated RFID transponder in various designs
- Accessories with RFID transponder
- RFID readers as interface to other IT systems and databases
There are special detectable cable ties for the food and pharmaceutical industry. Due to additional metal components, these can be detected with the help of metal detectors and X-ray equipment. For applications that require a particularly high degree of holding power and resistance due to adverse conditions, there are also cable ties made of stainless steel.