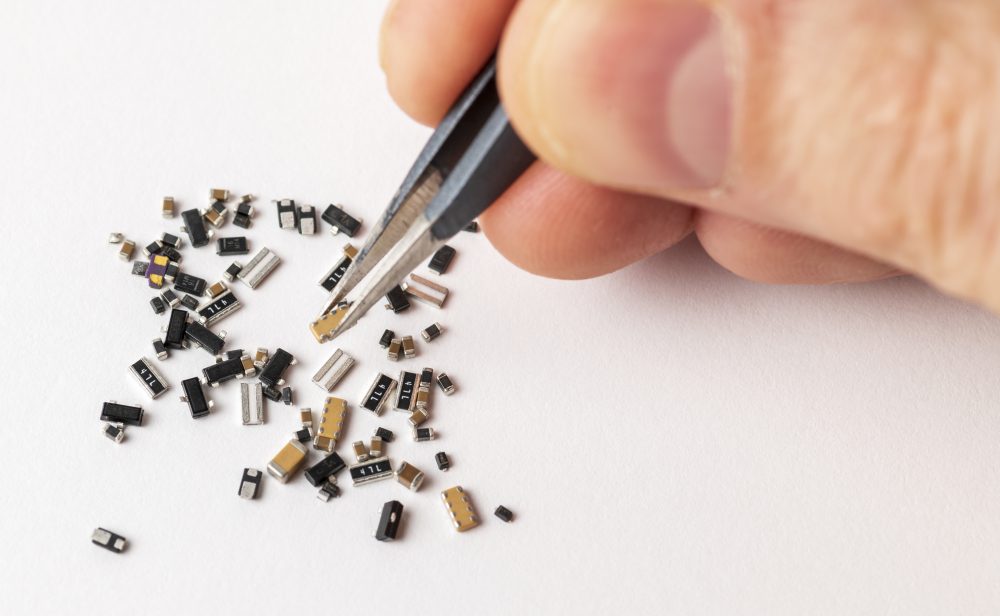
Focus on Miniaturization: The smaller, the better
The miniaturization trend is shaping the production of electronic and passive components like no other. The requirements for products: They need to be small, space-saving and yet more powerful than ever before. This often poses challenges for manufacturers, which they have to meet with innovative ideas. When did the miniaturization trend begin? And which components are currently particularly affected by this development? We provide information on these topics.
Miniaturization: the great history of small things
From the early days of electronics to the present day, a lot has happened in terms of the size of devices and components. Think of the first computers, for example: devices such as the ENIAC took up entire rooms. Nowadays, highly functional mini-computers are built into smartphones. This development towards ever smaller and more powerful devices and machines has been made possible by the miniaturization of electronic, semiconductor and connector components.
In the field of semiconductor technology in particular, small components have made a lot of progress. Miniaturization began when the first transistor was developed in 1947. This tiny component revolutionized electronics and led to the development of the integrated circuit (IC) in the 1960s. Suddenly thousands of transistors could be placed on a single chip, and that was just the beginning: ICs became smaller and more powerful over time. The smallest chip in the world, the Michigan Micro Mote, measures 2 by 2 by 4 millimetres.
Miniaturization: significance for electrical engineering and industry
Customer demands for more compact and powerful products have driven the electrical sector and industry to continuously innovate. Compact design is just as important as robustness – the small components must be able to continue working perfectly even in the event of vibrations and temperature fluctuations.
At the same time, they must be able to reliably transmit high currents and deliver the corresponding performance. It is also important to keep an eye on the price during production. After all, the production of small components involves a great deal of effort. At the same time, the various product categories place additional demands on the components. In connector technology, for example, it is important to guarantee the greatest possible flexibility and ensure easy handling.
For manufacturers, miniaturization therefore not only means smaller products, but also more efficient production, lower material consumption and ultimately more competitive models. It is a constant quest for perfection, where every micrometer and every millisecond counts.
The advantages at a glance
With smaller components come a multitude of possibilities and opportunities:
- Improved performance: miniaturization has led to a real surge in innovation in technology development. The Internet of Things (IoT) would not have been possible without the trend towards smaller, more powerful components.
- Greater functionality: Due to the compact design, the devices in which the miniaturized components are installed can also be smaller. This leads to improved functionality and ultimately to a better user experience.
- Lower energy consumption: Small components generally require less energy.
The challenges at a glance
While miniaturization offers numerous advantages, it also poses technical challenges, which the respective manufacturers have to meet with innovative ideas:
- Technical limits: As components shrink, it becomes more difficult to manufacture them with the same precision and reliability as their larger counterparts. For example, leakage currents can occur. These arise due to the ever thinner silicon dioxide layers used for the gate of the transistors. The result of leakage currents: more waste heat and higher power consumption. With several million transistors per chip, this inevitably leads to economic problems.
- Heat dissipation: One of the biggest challenges in miniaturization is heat dissipation. As the components become smaller on the one hand and closer together on the other, the heat output per unit area increases. The result: heat dissipation becomes a critical problem. Effective heat management is essential, especially in the area of printed circuit boards.
- Cost and manufacturing aspects: The search for new manufacturing methods, research into new materials and the conception of innovative product ideas: Investing in new techniques is costly and time-consuming. In addition, the requirements for precision and purity in production are becoming increasingly stringent. However, this makes investments necessary, including in advanced, specialized manufacturing technologies and equipment.
- Quality assurance: Due to their small size, micro components are more difficult to maintain and test. Quality management is becoming increasingly complex, as even large defects are very difficult to detect and rectify.
Miniaturization: Innovations in connector technology
In the field of connectors, which are essential for connecting electronic components, remarkable progress has been made in recent years in terms of their size.
- Lighter and smaller industrial connectors: Modular and miniaturized solutions were particularly needed in the field of heavy industrial connectors. Innovative product developments have made it possible to select the right rectangular connector for industrial applications more flexibly. The result: space savings of up to 50 percent. In addition, industrial connectors continue to become lighter and more flexible to use.
- Board-to-board connectors: With the trend towards ever smaller devices, the distances between circuit boards are also becoming shorter. New connector designs make it possible to connect boards at very close intervals or even in stacks without compromising performance.
- Improved materials: new plastics ensure longer connector life.
Miniaturization: a trend here to stay
Miniaturization is more than just a fad. It is a testament to human innovation and aspiration. With every step we take towards smaller, more powerful technology products, we open the door to new possibilities and applications that were previously unimaginable. Whether in semiconductor or connector technology – innovative product developments, research into new materials and a surge of innovation in production technology guarantee the expansion of application areas – and even more powerful devices, machines and systems.